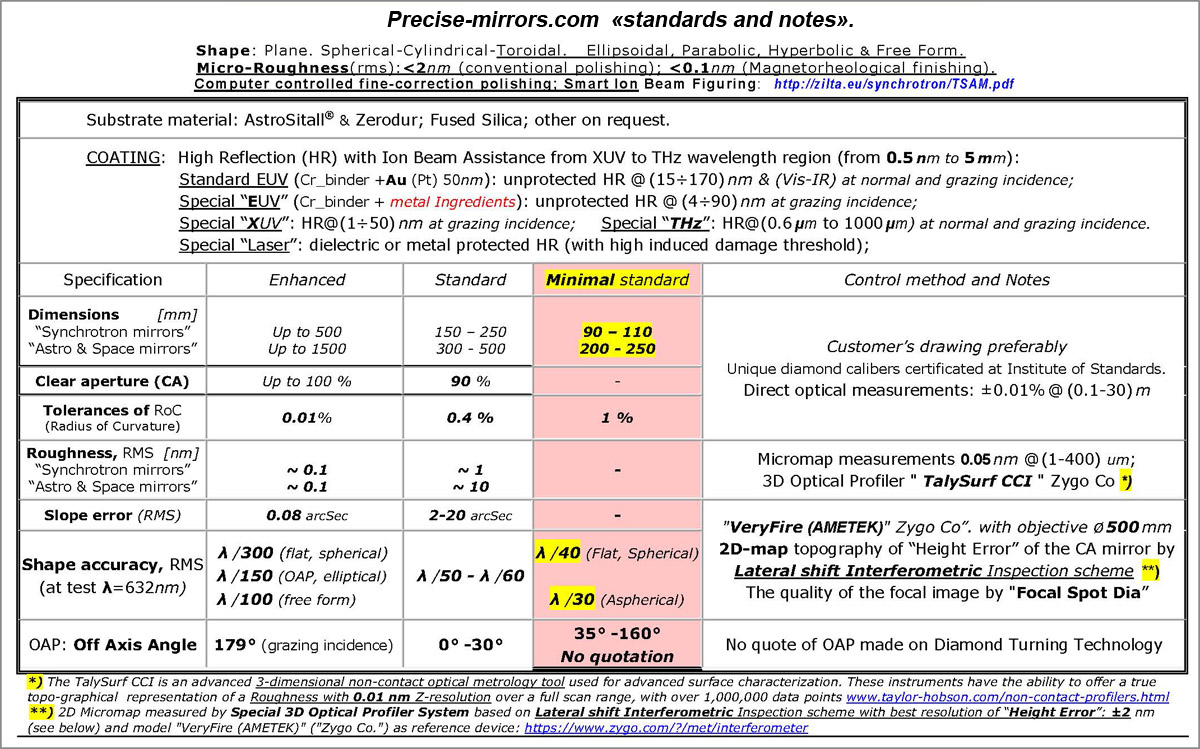
The most widespread are two types of optical coatings: metal and dielectric.
Mirrors with a metal coating make it possible to use them in a very wide spectral range (from 450 nm to 12 μm).
They are weakly sensitive to polarization and incidence
angle and also provide the same phase shift, making them suitable for ultrashort pulse applications.
However, these mirrors are more difficult to clean
and have a relatively low
Laser Induced Damage Threshold
(LIDT).
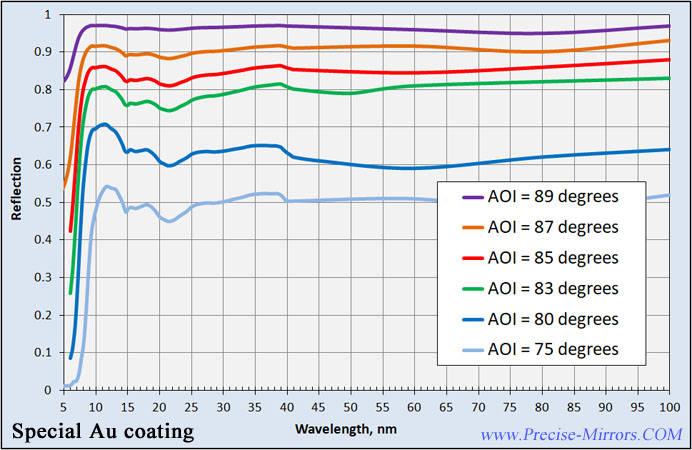
At high angles of incidence (more than 70-80 degrees),
some metal coatings can be used to work in
XUV spectral range (see below Au
reflection depends on AOI).
Therefore, special metal coatings are often used to
manufacture mirrors work in the shortwaves spectral range.
Dielectric mirrors offer higher reflectivity over a broad spectral range of a few 100 nm. Their coating is more durable, making them easier to clean, and more resistant to laser damage. However, standard dielectric mirrors have several disadvantages.
First of all,
dielectric mirror coatings can cause significant dispersive effects for ultrashort pulses,
that can broaden and distort short pulses (this problem is partially solved by the use of so-called "ultrafast dielectric coatings").
Secondly, dielectric mirrors are not suitable for use in the short-wave spectral range (wavelengths less than 200-250 nm).
Upon reaching a certain threshold value of the energy density
(LIDT) on the surface of the mirror,
reflective coating damage occurs.
The exact value of this
LIDT depends both on
--- the mirror itself (the type of reflective coating, the quality of coating and the manufacture of the mirror) and
--- on the radiation parameters (pulse
energy, duration and frequency, work spectral range, total irradiation area,
total continuous irradiation time and some
other parameters).
The highest LIDT
values are for dielectric
mirrors,
the average "typical value" is 5-20 J/cm2 (1064 nm, 10 ns, 10 Hz, 1 mm2)
or about 3-20 kW/cm2 for CW radiation (1064 nm, 1 mm2).
Mirrors
with metallic coatings (non metallic substrate)
have a lower LIDT,
the average "typical value" is 0.5-2 J/cm2 (1064 nm, 10 ns, 10 Hz, 1 mm2)
or about 0.5-1 kW/cm2 for CW radiation (1064 nm, 1 mm2).
Using various methods, it is possible to obtain higher LIDT values, for example, for dielectric mirrors to obtain
up to 50-150 kW/cm2 (CW 1064 nm) and 70-90 J/cm2 (10 ns, 1064 nm).
IMPORTANT!
When you change the wavelength, pulse duration or irradiation area size - the LIDT value changes strongly
nonlinearly,
so only a specialist should make an assessment of the LIDT for your radiation parameters.
YES, it's possible but please note in this case that we cannot guarantee a high LIDT. The damage threshold depends, among other things, on the quality and method of mirror substrates manufacture, which we cannot control in this case.
|
How to know the price of coating You need?You need Then send us Your specification by email to quote@precise-mirrors.com. |
You
may send your request in any form,
but to speed up the process of preparing a
quote, it
is better to fill out a special "request
form".
You may send additional data for the mirror as additional files in attachment to Your request.