On Axis Parabolic (hereinafter - parabolic) mirrors is central part of the surface of paraboloid of revolution.
Parabolic
mirrors are most commonly used for focusing collimated beam to obtain
minimal focal point size
or
inverse task -
when customer needs to
obtain collimated beam from
point source .
Upon reaching a certain threshold value of the energy density
(LIDT) on the surface of the mirror,
reflective coating damage occurs.
The exact value of this
LIDT depends both on
--- the mirror itself (the type of reflective coating, the quality of coating and the manufacture of the mirror) and
--- on the radiation parameters (pulse
energy, duration and frequency, work spectral range, total irradiation area,
total continuous irradiation time and some
other parameters).
The highest LIDT for simple dielectric
mirrors,
the average "typical value" is 10-20 J/cm2 (1064 nm, 10 ns, 10 Hz, 1 mm2)
or about 3-20 kW/cm2 for CW radiation (1064 nm, 1 mm2).
Mirrors
with metallic coatings (non metallic substrate)
have a lower LIDT,
the average "typical value" is 0.5-2 J/cm2 (1064 nm, 10 ns, 10 Hz, 1 mm2)
or about 0.5-1 kW/cm2 for CW radiation (1064 nm, 1 mm2).
Using various methods, it is possible to obtain higher LIDT values, for example, for dielectric mirrors to obtain
up to 50-150 kW/cm2 (CW 1064 nm) and 70-90 J/cm2 (10 ns, 1064 nm).
IMPORTANT!
When you change the wavelength, pulse duration or irradiation area size - the LIDT value changes strongly
nonlinearly,
so only a specialist should make an assessment of the LIDT for your radiation parameters.
The advantage of
parabolic mirrors is complete absence of spherical aberrations
(see figure below) and, accordingly,
the possibility of obtaining a diffraction-limited spot
(or "ideal" parallel beam) in any configuration.
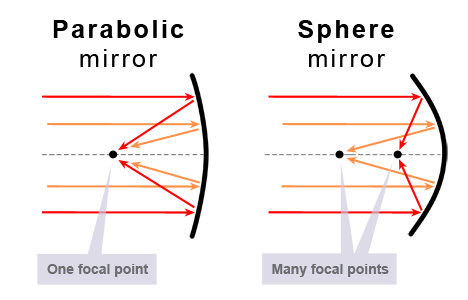
The disadvantage of parabolic mirrors (versus spherical mirrors) is higher cost and longer delivery terms.
Usually, it is very important for the customer
how small a spot in the image plane can be formed by the mirror.
Even if task is inverse (i.e. - "ideal"
collimated output beam),
this parameter allows you
to estimate important data about output beam
divergence.
Also, in some tasks the customer is often interested in the possibility of
obtaining an "ideally flat wavefront" in a collimated beam obtained after reflection from a mirror.
Be sure to specify whether you need this in your request for the cost of the mirror,
as this can significantly affect the price of the mirror.
The
spot size in the image plane for parabolic mirror depends on tolerance of the mirror surface shape
manufacturing and
diffraction limitations at the operating wavelength.
The general principle is that the closer the spot size to the diffraction limit, the more expensive the mirror is.
|
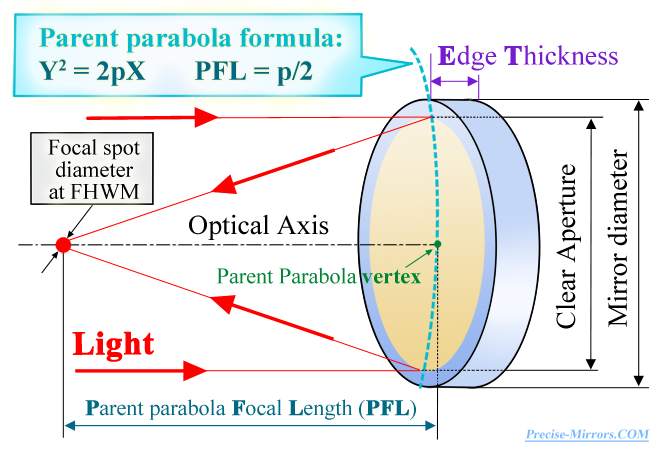
What are the minimal mirror parameters do you need to know to order?You need for Your working spectral range to choose:
A). Parent Parabola Focal Length
(PFL)
and diameter of a mirror (see the picture
above);; |
You
may send your request in any form,
but to speed up the process of preparing a quote, it is better to fill out a special "request
form".
You may send additional data for the mirror as additional files in attachment to Your request.