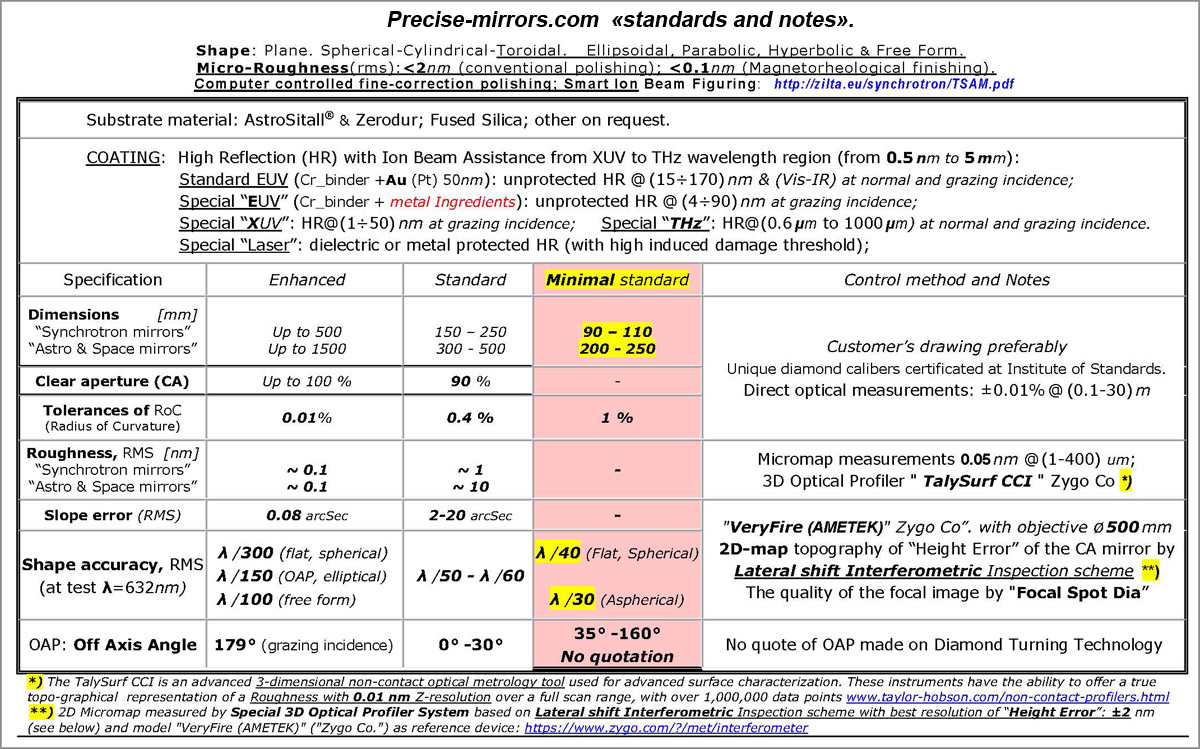
A toroidal mirror is part of the surface of a torus ("bagel").
Toroidal mirrors are often used when
customer works in short spectral wavelength
range
with standard task
to focus the radiation incident on the mirror at a large
AOI (about 60-89 degrees).
Less commonly, toroidal mirrors are used to obtain a relatively collimated
beam from point source.
The advantage of toroidal mirrors is their relatively low cost and fast delivery terms.
The disadvantage of toroidal mirrors is the presence of spherical aberrations,
which may sometimes lead to "a very bad
result" (even for ideal surface manufacture).
Usually, it is very important for the customer how small a spot in the image plane can be formed by the mirror (see the figure below). Even if a design is used where S' is infinity (collimated beam after reflection), this parameter allows you to estimate important data.
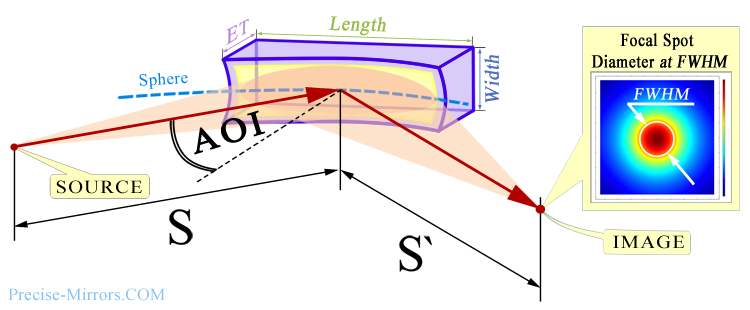
The spot size in the image plane can be affected by spherical aberrations, the precision of the mirror surface shape manufacturing,
as well as diffraction limitations at the operating wavelength.
The general principle is that the closer the spot size to the diffraction limit, the more expensive the mirror is.
|
What are the minimal mirror parameters do you need to know to order?You need for Your working spectral range:
A). decide on a combination of S,
S' and AOI (see the picture above,
here
pdf help guides); |
You
may send your request in any form,
but to speed up the process of preparing a quote, it is better to fill out a special "request
form".
You
may send additional data for the mirror
(mirror substrate material, tolerance of mirror
surface figure, desirable tangential and
sagittal radiuses, and etc.).